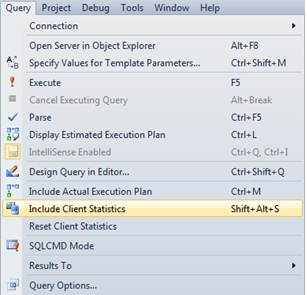
A feature often overlooked while tuning queries is Client Statistics located right on SSMS editor bar.
![]()
Other ways of opening Client Statistics include:
SHIFT + ALT + S and Menu Bar – Query -> Include Client Statistics
Client Statistics is useful when the user needs to gather information about execution times, processing times, the amount of data sent between client and server, etc. it’s very easy to use. Simply turn it on using one of the methods above and execute your query.
In this example I’m using the following query:
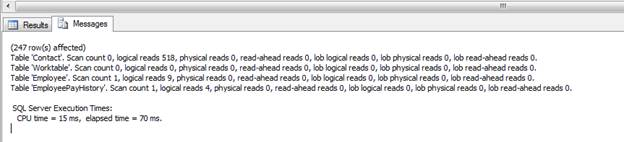
SELECT pc.FirstName ,pc.LastName ,pc.EmailAddress ,he.Title ,hh.Rate FROM Person.Contact pc JOIN HumanResources.Employee he ON pc.ContactID = he.ContactID JOIN HumanResources.EmployeePayHistory hh ON he.EmployeeID = hh.EmployeeID WHERE hh.Rate > 10 ORDER BY hh.Rate
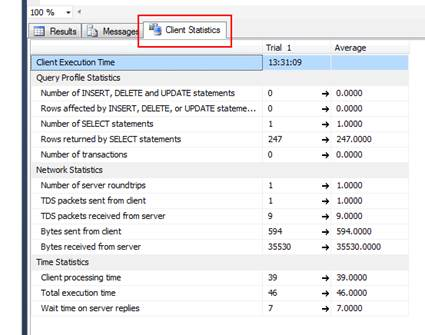
After executing the query you will notice a new tab labeled Client Statistics:
After looking at the statistics provided for Trial 1 you can see the processing time = 39ms, execution time = 46ms, etc.
After the running the same query again I get the following results under Trial 2:
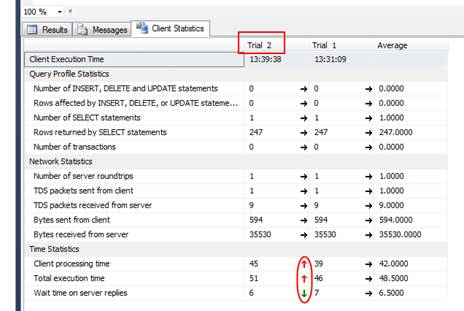
This time processing time went up to 45ms and execution time went up to 51ms. It also has an average column to compare overall results. The green and red arrows represent differences between trials. Green arrows indicate improved statistics and red arrows indicate degrading statistics.
A max of 10 trials can be run with the 11th trial dropping the 1st trial and so on. To reset statistics, on the menu bar, go to Query, Reset Client Statistics.
 This is great when tuning indexes because you can see different statistics as you add/delete indexes.
This is great when tuning indexes because you can see different statistics as you add/delete indexes.