I ran DBCC CHECKDB (Integrity Checks) in my maintenance plan and I also ran it manually, but I keep getting the error “The In-row data RSVD page count for object “table_name” , index ID 0, partition ID 58037252456448, alloc unit ID 58037252456448 (type In-row data) is incorrect.” How can I fix this error?
Solution
Before we discuss the simple steps to fixing this error, let’s discuss what might have happened in this situation.
Anytime you see an integrity check error it might make you a little queasy. No need to worry on this error. If you have recently upgraded from SQL Server 2000 then this error is somewhat common. I know what you’re saying, “Why is there a tip regarding SQL Server 2000?” Trust me, a lot of people are still running SQL Server 2000 which is now out of compliance with Microsoft, so everyone is in a rush to upgrade. Anyway, SQL Server 2000 used to update the page space used metadata. Once SQL Server 2005 came along, this was no longer the case so if you didn’t run DBCC UPDATEUSAGE after the upgrade/migration this error is likely to appear when you run DBCC CHECKDB.
Here is what the error message looks like:
Msg 2508, Level 16, State 3, Line 1 The In-row data RSVD page count for object "table_name", index ID 0, partition ID 58037252456448, alloc unit ID 58037252456448 (type In-row data) is incorrect. Run DBCC UPDATEUSAGE.
Running DBCC UPDATEUSAGE
If you notice in the maintenance plan or the DBCC CHECKDB results above, it displays “Run DBCC UPDATEUSAGE” after the error message. Ta da! After backing up your databases and establishing a maintenance window run DBCC UPDATEUSAGE (databasename). In a perfect world, SQL would notice this error and run DBCC UPDATEUSAGE on the appropriate table. This is not a perfect world, so we have to run it manually.
DBCC UPDATEUSAGE reports and corrects pages and row count inaccuracies in the catalog views. These inaccuracies may cause incorrect space usage reports returned by the sp_spaceused system stored procedure – MSDN.
DBCC UPDATEUSAGE (Apollo32_Fixed)
After running DBCC UPDATEUSAGE (databasename) on my questionable database you can see that all the page counts have been updated:
DBCC UPDATEUSAGE: Usage counts updated for table 'UserList' (index 'UserList', partition 1):
USED pages (In-row Data): changed from (5) to (4) pages.
DBCC UPDATEUSAGE: Usage counts updated for table 'UserRights' (index 'UserRights', partition 1):
USED pages (In-row Data): changed from (72) to (24) pages.
RSVD pages (In-row Data): changed from (80) to (33) pages.
DBCC UPDATEUSAGE: Usage counts updated for table 'UserRights' (index 'UserRights', partition 1):
USED pages (In-row Data): changed from (5) to (4) pages.
DBCC UPDATEUSAGE: Usage counts updated for table 'UserGroups' (index 'UserGroups', partition 1):
USED pages (In-row Data): changed from (4) to (3) pages.
DBCC UPDATEUSAGE: Usage counts updated for table 'Application' (index 'Application', partition 1):
USED pages (In-row Data): changed from (3) to (2) pages.
You only need to run DBCC UPDATEUSAGE once. After the page counts have been corrected your SQL Server will be back to normal. If you do not fix this issue right away, page counts will continue to get worse when data is added and will result in abnormalities in space usage reports.
After the update, running DBCC CHECKDB gives me a clean database again:
In essence, DBCC UPDATEUSAGE updates the used, reserved, and rows columns of the sysindexes (later named sys.indexes in SQL Server 2005) table.
In this example I have two databases named Apollo32 and Apollo32_Fixed. When running an integrity check against Apollo32 I get the error described above. Apollo32_Fixed is a copy of Apollo32 after running DBCC UPDATEUSAGE.
Before and After Comparison
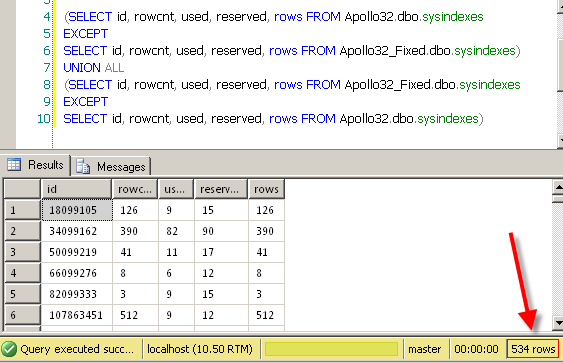
If I compare Apollo32.dbo.sysindexes to Apollo32_Fixed.dbo.sysindexes I can see I have 534 differences.
(SELECT id, rowcnt, used, reserved, rows FROM Apollo32.dbo.sysindexes EXCEPT SELECT id, rowcnt, used, reserved, rows FROM Apollo32_Fixed.dbo.sysindexes) UNION ALL (SELECT id, rowcnt, used, reserved, rows FROM Apollo32_Fixed.dbo.sysindexes EXCEPT SELECT id, rowcnt, used, reserved, rows FROM Apollo32.dbo.sysindexes)