In this post, I am going to outline my environment and then walk through the process of patching mirrored servers.
My test environment consists of two SQL Server 2005 SP2 servers named SSQL1 (principal) and SSQL2 (mirror) that contain eleven mirrored databases. The database mirroring operating mode is set to asynchronous and I’m upgrading to SP4.
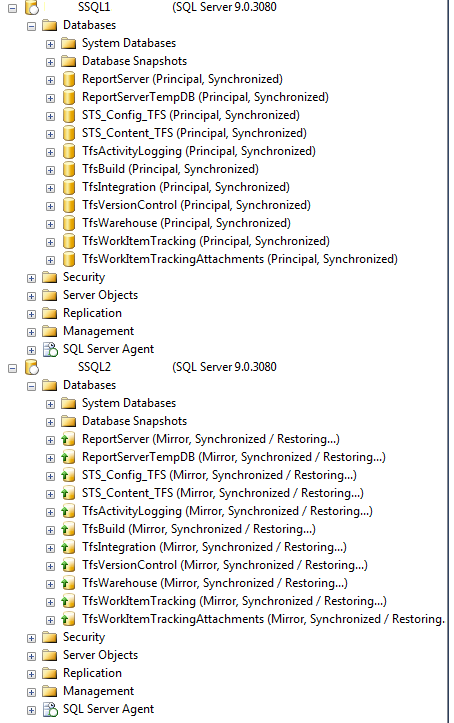
Here is a look at the two mirrored instances.
Step 1
Always backup all system and user databases before applying patches.
Step 2
Remote Desktop into the “Mirror” server (SSQL2 in our example) and download/copy the patch to the server.
Step 3
Stop all SQL Services on the “Mirror” server.
Step 4
Run the patch on the “Mirror” server.
Step 5
Once the patch is complete, reboot the “Mirror” server.
Step 6 (optional)
If your database mirroring is set to asynchronous (High Performance mode), we will need to synchronize the databases first. To do this we will need to issue the following statement for every database on the “Principal” server that is mirrored.
ALTER DATABASE databasename SET SAFETY FULL
Here are the commands for the 11 databases on my server.
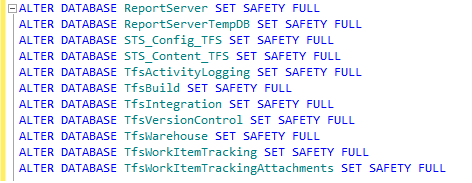 Step 7
Step 7
The databases might change to “synchronizing” while the transactions catch up. Once all of the databases show “synchronized”, as shown below, we can perform the manual failover.
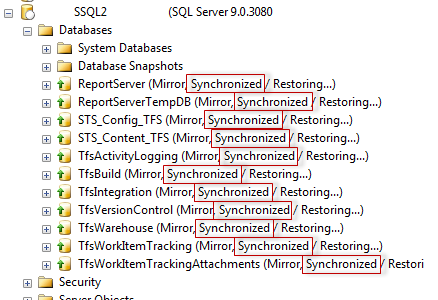
We can perform the failover using the following statement on the principal server for each database:
ALTER DATABASE databasename SET PARTNER FAILOVER
Here are the commands for the 11 databases on my server.
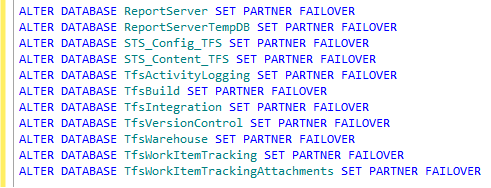
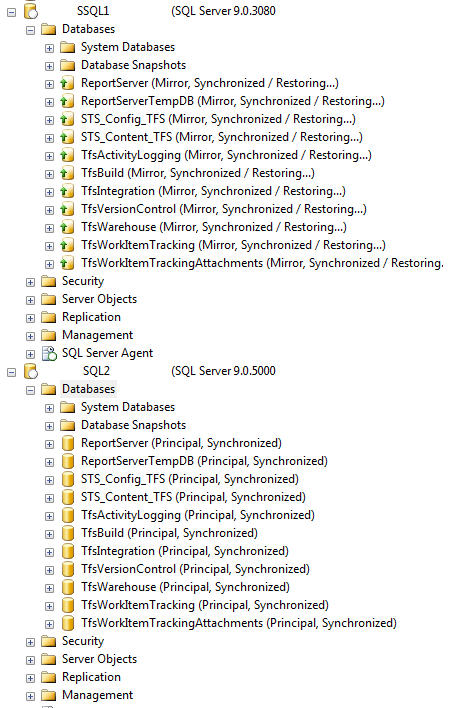
We can now see that the servers have switched roles.
Click here to view the rest of this post.